Makkah Al Mukarramah – Meaning, History and More
Makkah Al Mukarramah, colloquially known as Makkah, is undeniably the beating heart of the Islamic world. The holy city is home to nearly two million residents and hosts over three million pilgrims annually for Umrah or Hajj.
Makkah is an ancient city with profound significance to nearly two billion Muslims worldwide.
It’s the birthplace of the Holy Prophet, Muhammad PBUH, and houses the Kaaba, Islam’s focal point of worship, and the House of Allah SWT.
In this article, we’ll take a deep look into Makkah Al Mukarramah history and significance, sharing valuable insights to improve your knowledge and prepare you for your trip.
“And when We made the House a place of return for the people and [a place of] security.”
– Surah Al-Ankabut, 29:67.
What is the Meaning of Makkah Al-Mukarramah?
Makkah Al Mukarramah, also known as Mecca in the West and Makkah in the East, is a city in the Makkah Province of Saudi Arabia. It encompasses Islam’s most sacred structures, the Holy Kaaba, Masjid al-Haram and many more.
Muslims worldwide face towards the Kaaba during their daily prayers. Moreover, Hajj and Umrah pilgrims circumambulate (tawaf) it when fulfilling religious obligations like Hajj and Umrah.

Makkah Al-Mukarramah Meaning
Makkah Al-Mukarramah derives its name from Arabic. “Makkah” translates to “to surround” or “to encircle,” In ancient times, the city was surrounded by mountains and hills, providing a natural barrier against potential invaders.
Similarly, the term “Al-Mukarramah” translates to “the Honored” or “the Noble,” signifying its revered status.In pre-Islamic Arabia, the people of various tribes would gather in Makkah for various purposes.
The event brought peace to the region and allowed for trade and cooperation, reinforcing the sacredness of the city and its role as a center for religious unity and community-building.
Where is Makkah Located?
Makkah is nestled inland from the Red Sea, approximately 70 kilometers from the bustling port city of Jeddah. The city’s location is southwest of Saudi Arabia’s capital, Riyadh.
Makkah is surrounded by a mountainous terrain with rugged peaks and hills providing a natural enclosure.
As a result, it experiences a predominantly arid climate, with high temperatures exceeding 40°C and minimal rainfall throughout the year.
So, pilgrims planning to visit the city for Hajj or Umrah must plan accordingly to overcome the physical and spiritual challenges during their journeys seamlessly.
Staying hydrated is one of the key tips offered to staying healthy in Hajj to meet the demanding temperatures that Makkah offers. Pilgrims should avoid over-exerting themselves and could always try to avoid over-crowded areas
History of Makkah Before and After Islam

Before the advent of Islam, Makkah was a leading trading hub in the region. The city’s prime location near major caravan routes made it ideal for traders and travelers, connecting southern Arabia to the north and east.
The city was revered by various Arabian tribes due to the presence of the Kaaba, even before the time of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH).
However, in the pre-Islamic era, the city was marred by idol worship and tribal rivalries. Each tribe had its idols, and the Kaaba contained hundreds of them.
Despite the religious significance of the Kaaba, the essence of monotheism and the teachings of earlier prophets, like prophet Ibrahim (AS) and prophet Isma’il (AS), were obscured by polytheistic beliefs and practices.
The dawn of Islam marked a transformative moment in Makkah’s history. In 610 CE, Prophet Muhammad (SAW) received the first revelation of the Holy Quran in the Cave of Hira in the surrounding hills. These revelations challenged the prevailing idolatry and called for the worship of one true God, Allah (SWT).
After years of persecution and adversity, the city of Makkah witnessed a remarkable shift. In 630 CE, the Prophet Muhammad PBUH, along with a growing community of Muslims, returned to Makkah. He cleansed the Kaaba of its idols and reinstated the monotheistic worship of the one true God.
The city that had been a center of polytheism and idol worship became the epicenter of monotheism and Islamic faith.
Today, Makkah stands as a symbol of unity, drawing millions of Muslims from all over the world each year for the rituals of Hajj and Umrah. It’s a place where the oneness of Allah SWT is celebrated, and the tribal divisions of the past have given way to the universal brotherhood of Islam, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries.
What is the Kaaba (Black box) in Mecca?
The Kaaba, often called the “Black Box,” is the most sacred structure in Islam, situated within the Masjid Al-Haram, or the Grand Mosque, in Makkah. This cubic building stands at the heart of the holy city and holds immense historical and spiritual significance.
The Kaaba’s history dates back to the Prophet Ibrahim (AS) and his son Isma’il (AS). According to Islamic beliefs, Ibrahim (AS) and Isma’il (AS) were commanded by Allah SWT to construct the Kaaba as a house of worship dedicated to the one true God.
The Kaaba was initially built as a simple, unadorned structure. However, its transformation over the centuries is notable. The black silk and gold curtain that adorns the Kaaba, known as the kiswah, is changed annually.
It was in the 11th century that the tradition of covering the Kaaba with this black silk began. The black color signifies its humility and simplicity despite the covering’s luxurious material.
“The Kiswah is adorned with a gold band of ornamental calligraphy of the Quranic verses and every year during Hajj, the Kiswah is replaced with a white cloth that represents the Ihram of the pilgrims.”
The Kaaba is also tied to the rituals of Hajj, one of the Five Pillars of Islam, and Umrah. During these pilgrimages, millions of Muslims worldwide circumambulate the Kaaba in a counterclockwise direction, emulating the rituals of prophets, including prophet Muhammad (PBUH).
Why is Mecca important to Muslims?

Mecca is paramount to Muslims due to its role as the home of the Kaaba, often referred to as the House of Allah. Muslims, regardless of where they are in the world, pray in the direction of the sacred structure.
Mecca also connects Muslims spiritually, drawing them to the holy city for blessings, forgiveness, and a deeper connection with the Creator of the universe.
Are Non-Muslims Allowed in Mecca?
Non-Muslims are typically not allowed in Mecca. This restriction aims to preserve the sanctity of the holiest place in Islam. However, there are rare exceptions made for non-Muslims under specific circumstances.
In such cases, they must obtain special permits, follow strict guidelines, and are usually limited to certain areas.
These regulations are in place to ensure that the spiritual atmosphere and religious practices in Mecca remain undisturbed.
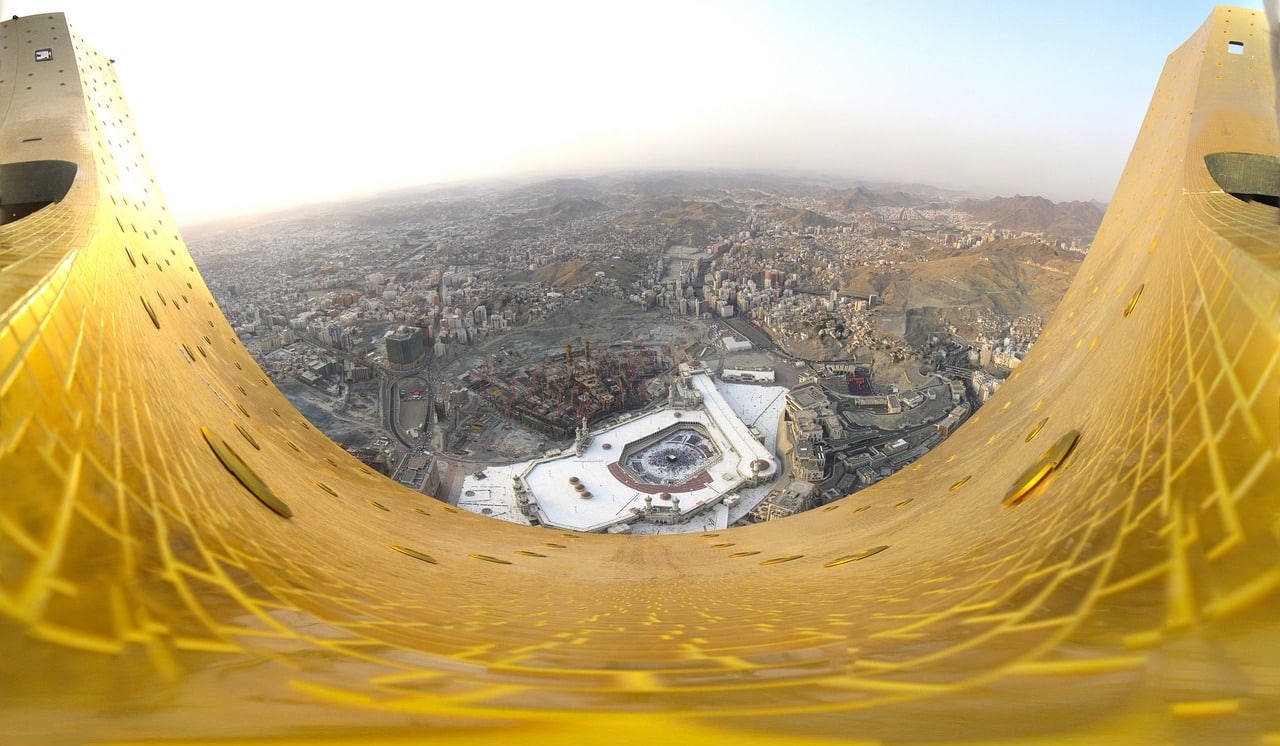
Pictures of Makkah Al Mukarramah
Below are some stunning pictures of different touchpoints in Makkah:
Makkah Al Mukarramah Hotels
Makkah Al Mukarramah offers a range of hotels to accommodate pilgrims who visit each year for Umrah and Hajj. Below are two popular hotels:
- Fairmont Makkah Clock Royal Tower
This luxurious hotel is part of the Abraj Al Bait complex and is known for its proximity to Masjid Al-Haram, the holiest mosque in Islam.
It’s just a short walk away, making it convenient for pilgrims. The hotel offers spacious rooms with stunning views of the Kaaba and the Haram, and its amenities include various dining options, shopping centers, and prayer areas.
- Swissotel Al Maqam Makkah
Situated in the Abraj Al Bait complex, this hotel is another popular choice among pilgrims. It’s directly facing the Masjid Al-Haram, allowing guests to have remarkable views of the holy Kaaba.
The hotel provides well-appointed rooms and suites, several dining options, and easy prayer access to the holy mosque.
Is Mecca Turning Green Now?

In the last decade, remarkable efforts have made Mecca greener and more sustainable. As part of the Saudi Vision 2030 plan, the “Greening the Desert” initiative has been launched, which includes extensive afforestation, landscaping, and irrigation projects.
This initiative aims to increase the city’s green spaces, reduce pollution, and create a more comfortable environment for residents and pilgrims.
“And He it is who produces gardens trellised and untrellised, and date palms, and crops of different shape and taste (its fruits and its seeds) and olives, and pomegranates, similar (in kind) and different (in taste). Eat of their fruit when they ripen, but pay the due thereof (its Zakat) on the day of its harvest, and waste not by extravagance. Verily, He likes not Al-Musrifun (those who waste by extravagance).” – Surah Al-An’am (6:141)
Also Abu Huraira reported: The Messenger of Allah, peace and blessings be upon him, said,
“The Hour will not be established until wealth is so abundant and overflowing that a man will go out with his wealth to give alms but not find anyone who accepts it from him, and until rivers and meadows return to the land of Arabia.”
Source: Sahih Muslim 157
Cities nearby Makkah
While Makkah Al Mukarramah remains the epicenter of Islamic spirituality, several cities in Saudi Arabia hold historical, cultural, and geographical significance.
Here are brief insights into some of the cities near Makkah:
- Al Madinah Al Munawwarah
Commonly known as Madinah or Medina, Al Madinah Al Munawwarah Holds a special place in Islamic history. It was where the Prophet Muhammad (SAW) and his people lived for years while seeking refuge from persecution.
It’s also the resting place of the final messenger of Islam. Today, this vibrant city continues to attract pilgrims and travelers, offering a profound connection to the roots of Islam.
- Taif
Taif, known for its pleasant climate and fragrant rose gardens, is significant in Islamic history. The city served as a sanctuary for the Prophet Muhammad (SAW) during a difficult period of his mission. It’s a tranquil destination for those visiting the region.
- Jeddah
Jeddah is the gateway to Makkah and a key entry point for pilgrims visiting Saudi Arabia. It’s a thriving, diverse city, blending modernity and history along the Red Sea coast. It boasts a vibrant cultural scene and is a hub for commerce.
- Tabu
Tabuk is renowned for its historical sites linked to early Islamic battles. It’s home to the Tabuk Castle, a well-preserved fortress from the Prophet Muhammad’s military expeditions. Pilgrims can explore its historical and architectural heritage.
- Riyadh
The capital of Saudi Arabia, Riyadh, is a political and economic hub and a center for education and culture. While not as close to Makkah as the other cities, Riyadh plays a vital role in the nation’s overall landscape.
Summary – Makkah Al Mukarramah
Located in the heart of Saudi Arabia, Makkah Al Mukarramah is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad (SAW) and home to the revered Kaaba, where millions of Muslims converge to fulfill their religious obligations.
So, whether you’re looking to visit for Umrah or Hajj, embark on your spiritual journey to the holiest city in Islam and visit the most important mosque in the world by booking one of our amazing packages.
Once you reach Makkah Al Mukarramah, you’ll feel a notable difference in your mind and body as your spiritual side awakens like millions of people have before. Reach to learn more about our service.
Through His Names
New course with
Ustadh Shabbir Hassan