Hajj Rituals & How to Perform Hajj a Step by Step Guide
What is Hajj?
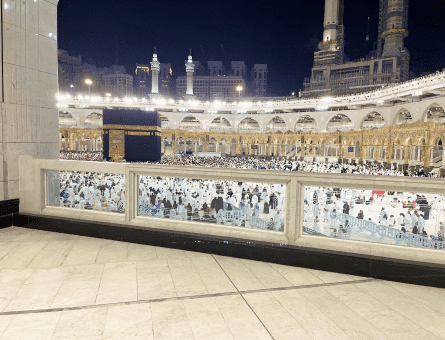
Hajj is the annual Islamic pilgrimage that is performed in Makkah, a sacred city in Saudi Arabia. This is an essential religious duty for Muslims. Every adult Muslim should perform Hajj at least once in his or her lifetime if they have the ability, physically and economically.
Pilgrimage means to go to a popular place. In Islam, Makkah is one of two holy cities, called the Haramain, along with Madinah. Hajj is performed in Makkah and its surrounding areas.
Hajj rituals are performed in five or six days, beginning on the 8th of Dhul Hijjah and ending on the 13th of this month, which is the 12th and last month of the Islamic calendar. Hajj is one of the five pillars of Islam, along with Shahadah, Salah, Zakah and Sawm.
The Hajj is the largest annual religious event where a large number of Muslims from all over the world and in their millions, gather in a sacred area of Saudi Arabia.
“Indeed, the first House [of worship] established for mankind was that at Makkah – blessed and a guidance for the worlds.” [Surah al-Imraan 3:96]
The condition of being physically and financially competent to perform Hajj is called istita’ah, and the Muslim who fulfills this condition is called mustati. Hajj means “to take part in the journey,” which signifies both the outward act of travel and the inner function of intention.
Since the Islamic calendar is lunar and the Islamic year is about eleven days shorter than the Gregorian year, the dates of the Gregorian Hajj changes from year to year. Hajj 2024 will begin on Friday the 14th of June 2024 and end on Wednesday the 19th of June 2024.
Hajj consists of some essential rituals that the pilgrim must perform. Let’s take a look at these important practices.
A step-by-step guide of the 9 significant Hajj rituals:
1. Ihram

The Ihram pictured above, consists of two unstitched white sheets for men. For women, an abayah is usually worn over the ihram. This should be worn before crossing Miqats.
2. Mina

Mina is a small town situated at a distance of 5 or 6 kilometres from Makkah. Another name of the town is the ‘City of tents‘. After leaving Makkah, pilgrims spend their first day and night in the tents of this city. This is the second ritual of Hajj where pilgrims spend whole day and night offering the prayers (compulsory and non-compulsory). These tents are equipped with almost all modern amenities.
3. Arafat

On the 9th day of Dhul Hijjah, pilgrims start their journey from Mina to Arafat. The distance from Makkah to Arafat is 18 kilometres but the distance from Mina to Mount Arafat is 12.9 kilometres. Spending time in Arafat is a very important ritual of Hajj and Mount of Arafat is called ‘Mount Mercy’ or ‘Jabal al Rahmah’, in Arabic.
At the place of this mount, the Prophet Muhammad (SAW) delivered his last sermon at the time of Hajj. Here, Muslims mostly make Istighfar and supplicate to Allah. They offer two prayers (Dhuhr and Asr) combinedly.
4. Muzdalifah

Muzdalifah is a town between Mount Arafat and Mina and it is next destination or ritual for Pilgrims after Arafat.
After sunset, pilgrims leave the Arafat for Muzdalifah where they offer two prayers (Maghrib and Isha) combinedly. They spend the whole night in the open sky and collect the pebbles for stoning ritual (rami) in the Muzdalifah. They leave this town on the morning of 10th day of Hajj.
The pilgrims head to Makkah for performing Tawaf al-Ifadah and Sa’i and then go back to Mina for performing Rami, Nahr and Halq.
5. Rami

Rami means throwing stones. This ritual is performed in Mina by throwing stones at 3 special pillars. The performance of this is repeated on 4th and 5th days of Hajj.
This process is a symbolic, it represents throwing stones at the shaitaan. In the story of Prophet Ibrahim (AS), the shaitaan tried to dissuade Prophet Ibrahim (AS) from following Allah’s commands. It is at these 3 places (the locations of the 3 pillars) where he tried to do this. So we throw stones here to represent us not giving in to the whispers of shaitaan.
6. Nahr- Sacrifice of Animals

The end of the stone ceremony calls for animal sacrifice. Apart from the pilgrims, it is also important act for all Muslims who are able to perform it.
7. Halq & Taqsir

Halq means shaving the head and Taqsir means cutting the hair a little. A man can select Halq and Taqsir but Halq is considered to be better. Women, on the other hand, partake in Taqsir. This ritual is performed on the 3rd day of Hajj.
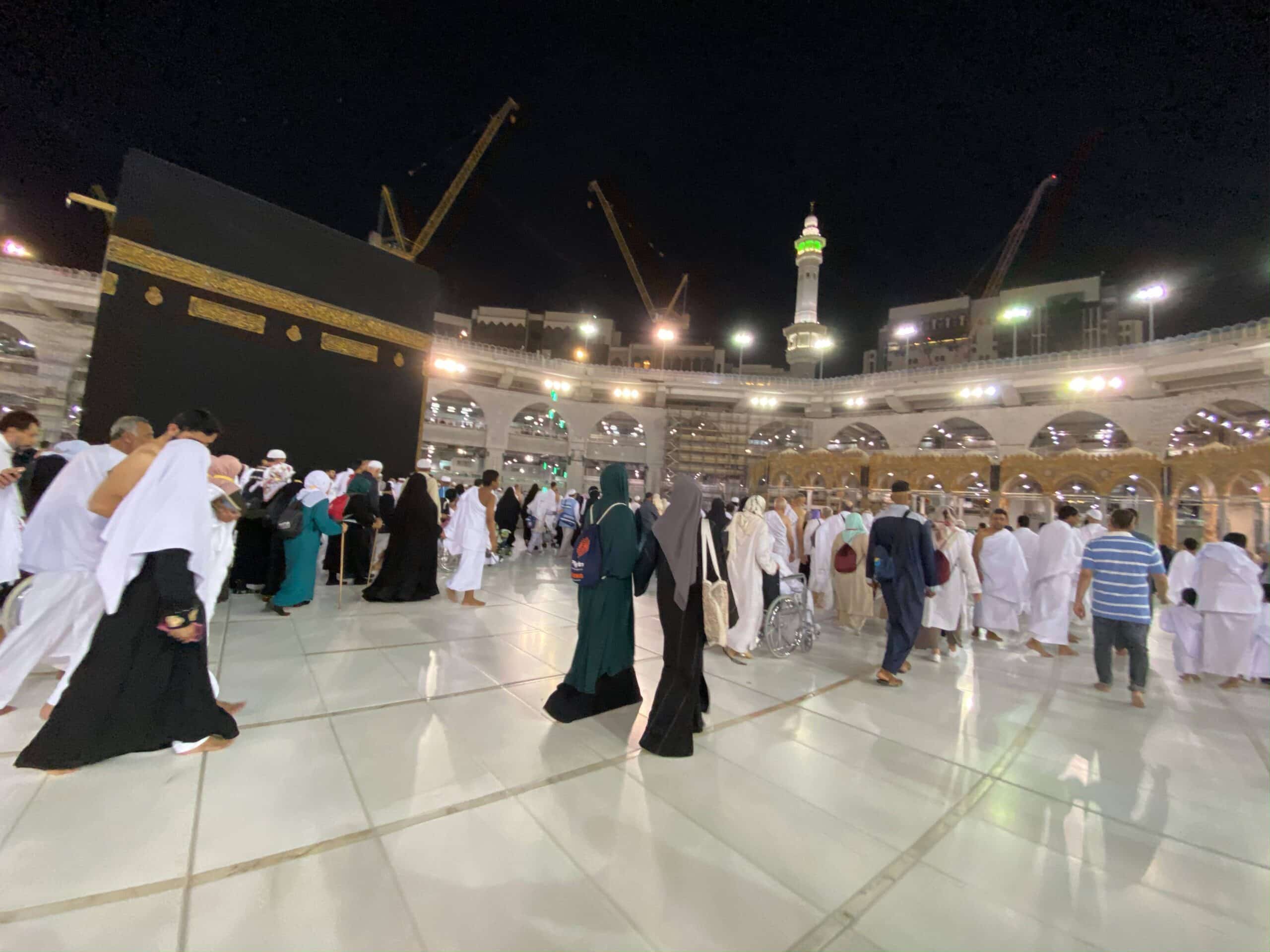
8. Tawaf & Sa’ee

Tawaf and Sa’ee are two rituals which are performed in Masjid-Al-Haram but the method is different. During the Tawaf, pilgrims circumambulate seven times around the Kaaba.
In the ritual of Sa’ee, pilgrims run (or walk fast) back and forth seven times between Safa and Marwah mounts.
Pilgrims perform these both rituals on 1st day or 8th day of Dhul Hijjah before leaving Masjid-Al-Haram for Mina and they repeat these both rituals on 3rd Day of Hajj after performing the Halq and Taqsir.
“Indeed, as-Safa and al-Marwah are among the symbols of Allah. So whoever makes Hajj to the House or performs ‘umrah – there is no blame upon him for walking between them. And whoever volunteers good – then indeed, Allah is appreciative and Knowing.” [Surah Al-Baqarah 2:158]
9. Farewell Tawaf
The Farewell Tawaf is the last ritual of Hajj and after performing it, pilgrims have completed their Hajj. This is performed in the same method as the Tawaf of pilgrims in Umrah and Hajj.
The performing Hajj is a very important physical and spiritual task. It has the ability to change peoples lives, for the better.
May Allah invite us all to His house, ameen.
Explore The New Pilgrim App
The Ultimate App
for Hajj and Umrah!